- BIS Certification for cement manufacturers ensures product quality, safety, and compliance under Indian Standards.
- The process covers ISI marking, factory audits, sample testing, and continuous surveillance.
- Manufacturers must meet BIS norms to legally sell cement in India and access major government projects.
Introduction

When a mid-sized cement grinding unit in Gujarat contacted our team, the owner was unsure why their product couldn’t participate in a government road project despite competitive pricing. The issue wasn’t quality—it was the absence of a BIS Certification for cement manufacturing, specifically the ISI licence under the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
This situation is common. Many cement factories perform rigorous in-house testing, invest in modern machinery, and follow global quality practices; yet without a BIS Licence, their cement cannot legally be sold in India. For manufacturers, BIS compliance is not a mere formality—it is the gatekeeper to the Indian construction market.
The following guide explains the BIS Certification process for cement manufacturers, the documentation, timelines, legal requirements, and the standards governing Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC), and Portland Slag Cement (PSC). This long-form reference has been written in a human advisory tone, aligned with Google search-quality standards and suitable for AI Overviews.
What is BIS Certification for Cement Manufacturers?
BIS Certification is an official approval issued by the Bureau of Indian Standards confirming that cement products meet the mandatory Indian Standards specified under IS codes. Cement is covered under the Compulsory Registration Scheme (CRS) for safety-critical products.
BIS Certification ensures uniformity in strength, fineness, chemical composition, soundness, setting time, and long-term durability—key factors influencing structural safety across India.
Understanding the ISI Mark for Cement Products
The ISI Mark is the compliance symbol that appears on each cement bag sold in India. It serves as a public assurance that the cement meets the prescribed performance standards such as:
- Grade strength (33, 43, 53)
- Setting time requirements
- Compressive strength
- Soundness and durability thresholds
In the construction ecosystem, engineers, contractors, and government bodies widely rely on the ISI Mark to filter compliant cement from unregulated products.
Key BIS Standards Applicable to Cement
The major Indian Standards applicable to cement certification include:
- IS 269 – Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
- IS 1489 (Part 1 & 2) – Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC)
- IS 455 – Portland Slag Cement (PSC)
- IS 12330 – Sulphate Resisting Portland Cement
- IS 16415 – Composite Cement
Each standard defines technical criteria, test methods, and quality parameters that manufacturers must meet throughout production.
Legal Framework Governing Cement Certification
BIS Certification is governed under:
- BIS Act, 2016
- BIS (Conformity Assessment) Regulations, 2018
- Quality Control Orders (QCOs) issued by the Ministry of Commerce
Under these regulations, no cement bag can be manufactured, stored, packed, imported, or sold without a valid BIS Licence. Non-compliance can attract legal action, including penalties and factory closure orders.
Why is BIS Certification Mandatory for Cement Manufacturers?
Mandatory certification was introduced to protect consumers and ensure India’s infrastructure is built on safe, reliable materials.
Mandatory Requirements under BIS Act
The BIS Act enforces compulsory certification for cement due to:
- High public safety implications
- Potential risks linked to substandard construction
- National interest in standardizing critical raw materials
Any manufacturer supplying cement without ISI approval is considered in violation of the Act.
Ensuring Public Safety Through Standardized Cement Quality
Cement quality directly impacts building lifespan, earthquake resistance, bridge stability, and road durability. Standardised cement reduces:
- Structural failures
- Water permeability issues
- Cracking and shrinkage
- Premature deterioration
Standardisation ensures that every cement bag performs consistently, irrespective of the manufacturing unit.
Government Regulations & Market Entry Compliance
To participate in:
- CPWD projects
- State PWD contracts
- Smart City developments
- Railways, metro, airport, and NHAI construction
manufacturers must hold a valid BIS Certification. Without it, even high-grade cement is automatically disqualified.
Benefits of BIS Certification for Cement Manufacturers
Enhanced Brand Trust & Market Acceptance
Distributors, contractors, and procurement agencies prefer suppliers with BIS Licences. The ISI mark builds immediate trust and widens market reach.
Improved Product Quality & Consistency
Factories aligned with BIS norms typically experience:
- Stable compressive strength
- Lower test variations
- Improved kiln and grinding control
- Reduced batch rejections
Quality consistency reduces customer complaints and warranty issues.
Eligibility for Government Tenders & Large Projects
Certification unlocks eligibility for:
- Government infrastructure projects
- Corporate and private turnkey projects
- Institutional contracts
It positions the manufacturer as a compliant and reliable supplier.
Cement Products Which Require BIS Certification
List of Cement Types Under Mandatory BIS Scheme
The following cement products require BIS Certification:
- OPC 33, 43, 53 grade
- PPC Fly Ash Based & Calcined Clay Based
- PSC
- Composite Cement
- White Cement
- Rapid Hardening Portland Cement
Standards Applicable to OPC, PPC & PSC Cement
Each grade must meet:
- Fineness
- Initial and final setting time
- Strength at 3, 7, and 28 days
- Soundness via Le-Chatelier method
- Alkali limits
These parameters are verified through standardized testing.
Exemptions and Special Category Cement Products
Exports may receive exemptions under certain conditions; however, domestic sales always require ISI certification. Some specialty cements not used for structural purposes may qualify for conditional exemptions, depending on BIS guidelines.
Documents Required for BIS Certification for Cement Manufacturers
Technical Documents Needed for ISI Mark Licensing
Common technical documents include:
- Product specifications
- List of raw materials
- Manufacturing flowchart
- Calibration certificates
- In-house laboratory data
Manufacturing & Quality Control Documents Checklist
BIS requires evidence of a functioning quality system:
- Quality control manuals
- Process control charts
- Daily production records
- Internal test reports
Factory Infrastructure and Testing Equipment Requirements
The factory must maintain fully equipped testing laboratories capable of conducting tests prescribed under IS standards, including:
- Blaine fineness apparatus
- Compression testing machines
- Autoclave soundness equipment
- Vicat apparatus
BIS inspectors verify that instruments are in working condition and calibrated.
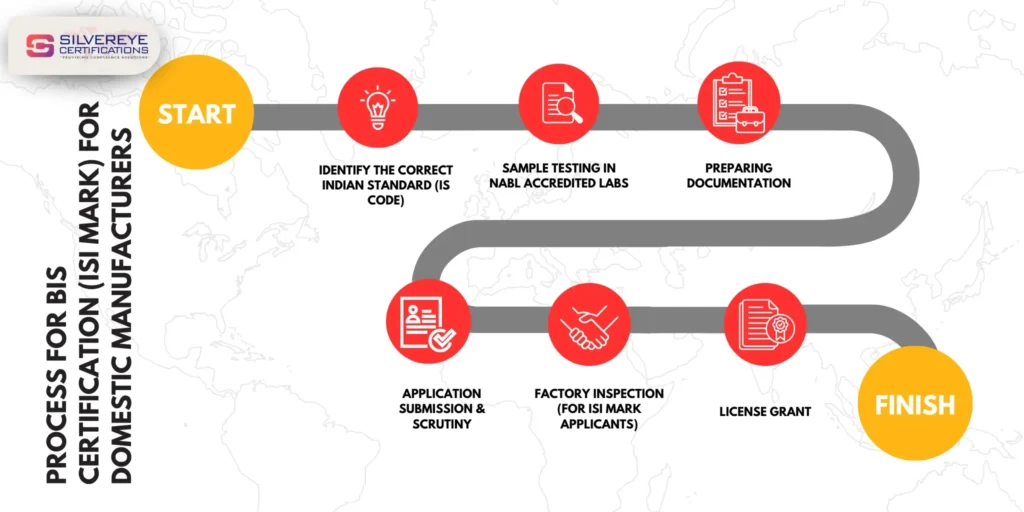
Process for BIS Certification for Cement Manufacturers
Step-by-Step Procedure for ISI Mark Licensing
- Online application submission
- Uploading documents
- Payment of fees
- Factory audit scheduling
- Product sampling and independent laboratory testing
- Compliance assessment
Factory Audit & Sample Testing Workflow
A BIS officer visits the manufacturing unit to inspect process control, plant layout, production capacity, and laboratory facilities. Random samples are collected and tested in a BIS-recognised lab.
Grant of License and Post-Certification Obligations
Upon successful evaluation, BIS issues the licence along with a unique ISI marking number. Manufacturers must comply with surveillance audits and periodic testing to retain the licence.
ISI Marking for BIS Certification for Cement Manufacturers
Guidelines for Using ISI Mark on Cement Bags
ISI mark placement, label size, and positioning must follow BIS guidelines. The licence number should be clear and readable.
Packaging, Labeling & Marking Requirements
Mandatory details include:
- IS Standard number
- Manufacture date
- Grade
- Batch number
- Net quantity
Handling Misuse or Non-Compliance of ISI Mark
Improper use of the ISI mark can lead to prosecution under the BIS Act, fines, and cancellation of the licence.
BIS Certification Cost and Timeline
The cost of BIS Certification for Cement depends on factory size, number of grades, and testing requirements. Costs generally fall into three categories: BIS fees, testing charges, and audit/travel expenses.
BIS Application Fees and Testing Charges
| Fee Type / Cost Component | Indicative Amount (₹) | Remarks / Source |
| Application fee (new ISI licence) | ₹ 1,000 | Standard non-refundable fee for product certification. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Annual licence fee (domestic manufacturer) | ₹ 1,000 (per year) | Applicable for maintaining ISI licence. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Audit / Factory Inspection fee | ₹ 7,000 per man-day | BIS charges applicable man-day audit fee (for inspection/surveillance) under Scheme I. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Sample testing fee (initial / certification testing) | As applicable | Charges vary depending on number of tests, cement grade (OPC, PPC, PSC), and lab rates. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Marking (Standard-Mark / ISI) fee | As per BIS marking fee schedule | Marking fee depends on IS standard and quantity/volume (cement production volume). (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Renewal application fee | ₹ 1,000 (non-refundable) | For licence renewal under standard BIS fee structure. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
Testing fees vary according to grade selection and lab location.
Factory Inspection and Audit Cost
BIS charges manufacturers for:
- Auditor travel and lodging
- Inspection time
- Additional sampling if required
Remote factories may incur higher inspection costs.
Expected Processing Time for BIS License
Typical timelines:
- Document preparation: 7–10 days
- BIS scrutiny: 10–15 days
- Factory inspection: 15–20 days
- Testing and report review: 10–25 days
Most manufacturers receive the license within 45–60 days with proper planning.
BIS License Validity and Renewal
Once granted, a BIS License for Cement remains valid for a defined period, subject to renewal and compliance checks.
Standard Validity Period of BIS License
The initial license is usually valid for two years. Subsequent renewals can extend validity up to five years, depending on compliance performance and timely submission of documentation.
Renewal Procedure and Documentation
The renewal process involves:
- Submission of updated factory details
- Past audit reports
- Production records
- Test reports from in-house and external labs
- Fee payment
Manufacturers must apply for renewal before license expiry to avoid penalties.
Late Fee and Compliance Requirements
Delayed renewal results in:
- Late fees
- Possible suspension of the license
- Mandatory re-inspection in certain cases
Many manufacturers proactively renew six months before expiry to avoid disruptions during peak supply seasons.
Silvereye Certifications supports many plants during renewal to ensure continuity.
Conclusion
BIS Certification for cement manufacturers remains a non-negotiable requirement in India’s construction ecosystem. From market acceptance to government tender eligibility, an ISI licence defines whether a cement brand can participate in mainstream supply chains.Manufacturers who follow the BIS process precisely—supported by expert partners such as Silvereye Certifications—experience smoother audits, faster approvals, and greater long-term stability. Ensuring compliance with BIS standards is not just a regulatory obligation; it is an essential investment in brand credibility and market expansion.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is BIS Certification for Cement Manufacturers?
BIS Certification ensures that cement products meet the mandatory Indian Standards for strength, durability, composition, and safety.
Is BIS Certification mandatory for selling cement in India?
Yes. Cement is covered under compulsory BIS Certification, and no manufacturer can sell cement without a valid ISI licence.
Which Indian Standards apply to cement products?
Common standards include IS 269 (OPC), IS 1489 Part 1 & 2 (PPC), IS 455 (PSC), and IS 16415 (Composite Cement).
What documents are required for BIS Certification?
Technical specifications, manufacturing process flow, QC procedures, calibration reports, and internal test results.
How long does the BIS Certification process take?
Typically 30–90 days, depending on audit readiness, sample testing, and documentation accuracy.
What happens during the BIS factory audit?
BIS inspects the production line, quality control systems, in-house lab setup, and collects random samples for testing.
Can cement be sold without an ISI Mark?
No. Selling cement without the ISI Mark violates the BIS Act and can lead to penalties or closure.
What is the validity of a BIS Licence for cement plants?
The licence is valid for 1–2 years and must be renewed before the expiry date.
What are the major costs involved in BIS Certification?
Application fees, audit charges, testing fees, and annual marking fees based on production capacity.
Why do manufacturers take help from experts like Silvereye Certifications?
To avoid documentation errors, prepare for audits, ensure compliance, and speed up licence approval.















