- BIS Standards for Cement define the mandatory quality, chemical, and strength requirements every cement manufacturer in India must follow.
- These Cement IS Standards ensure uniform performance, structural safety, and legal market compliance under the ISI Mark for Cement.
- Manufacturers rely on BIS norms to maintain consistent quality, reduce failures, and meet procurement eligibility across major construction sectors.
Introduction

A cement manufacturer from Rajasthan once contacted us after a major infrastructure contractor rejected an entire shipment due to inconsistent compressive strength. Their internal tests showed borderline results, but BIS surveillance sampling told a different story. The plant did not fully adhere to BIS Standards for Cement—specifically the prescribed limits for setting time and chemical composition.
Incidents like this demonstrate why Indian Standards for Cement are more than regulatory instructions. They act as quality boundaries that protect structural integrity across roads, bridges, metro corridors, and residential projects. When manufacturers follow these BIS norms consistently, they experience better market acceptance and fewer disputes with contractors.
Overview of Cement Quality Control in India
Cement quality standards in India are stringent because the material directly influences structural stability. Plants must maintain continuous monitoring of fineness, strength, pozzolanic content, and raw material quality. Deviation in any parameter—however small—impacts on-site performance.
India’s cement sector has grown rapidly, but BIS Standards ensure that growth does not compromise quality.
Role of BIS in Standardising Cement Manufacturing
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is responsible for regulating cement quality under the ISI Scheme (Scheme-I). BIS conducts inspections, verifies production capability, examines laboratory calibration, and ensures every bag leaving the plant matches the approved standard.
This oversight helps maintain uniformity across thousands of plants nationwide, from large integrated units to grinding stations.
Why Cement Standards Influence Structural Safety
Cement is a safety-critical material. Variations in compressive strength, setting time, or soundness can lead to cracks, moisture penetration, or long-term structural degradation. BIS Standards create predictable performance, helping engineers design structures with confidence.
What are the BIS Standards For Cement?
BIS Standards for Cement are formal Indian Standards (IS codes) defining minimum quality, performance, testing methods, and manufacturing conditions for each type of cement. They ensure that cement performs reliably across different climatic zones and construction applications.
Definition and Purpose of BIS Cement Standards
BIS Standards protect life, property, and national infrastructure by prescribing clear limits for strength, chemical composition, and durability. They also prevent quality fluctuations caused by seasonal changes, raw material variation, or machinery ageing.
Key Quality Parameters Covered Under BIS Norms
All Cement IS Standards cover parameters such as:
- Specific fineness
- Normal consistency
- Initial & final setting time
- Compressive strength (3, 7, 28 days)
- Soundness
- Ratio of clinker, gypsum, slag, or fly ash
- Chemical limits: chloride, magnesia, sulphur trioxide, alkalis
These parameters form the backbone of cement quality control.
How BIS Standards Ensure Product Consistency
BIS mandates batch-wise testing, calibrated instruments, and documented QC practices. Regular BIS surveillance sampling ensures manufacturers maintain consistent performance—not just during certification but throughout production.
Why are the BIS Standards For Cement Mandatory?
India mandates compliance with BIS Standards to guarantee uniform construction safety nationwide.
Safety and Structural Integrity Requirements
BIS norms ensure cement can withstand loads, resist environmental impact, and maintain long-term durability. Structures built with non-standard cement face higher risks of shrinkage cracks, rapid deterioration, and reduced lifespan.
Legal Compliance for Cement Manufacturing Units
Under the BIS Act, no manufacturer can sell cement without a valid BIS license. Non-compliance may lead to penalties, seizure of goods, or suspension of manufacturing operations.
Preventing Substandard and Fake Cement in the Market
Counterfeit cement bags and low-grade material remain a challenge in several regions. BIS Standards and ISI Marking prevent such products from entering the supply chain.
BIS Standards You Must Know for All Major Cement Types in India
Each cement type has a dedicated IS code specifying its chemical and physical requirements.
BIS Standards for OPC, PPC, PSC and Composite Cement
- OPC: IS 269 (33 Grade), IS 8112 (43 Grade), IS 12269 (53 Grade)
- PPC: IS 1489 (Part 1 & 2)
- PSC: IS 455
- Composite Cement: IS 16415
Chemical, Physical and Strength Requirements
Every category has specific strength limits, fineness requirements, and chemical composition boundaries. For example, OPC 53 must achieve higher early strength, while PPC must meet pozzolana content requirements.
Differences in BIS Standards for Each Cement Category
- OPC focuses on strength and early setting performance.
- PPC emphasises long-term durability through pozzolanic reactions.
- PSC offers enhanced resistance to sulphate and chloride attack.
- Composite cement balances environmental efficiency and performance.
Complete List of BIS Standards for Cement
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has defined a comprehensive set of standards to regulate the quality, safety, and performance of different types of cement used across construction and infrastructure projects in India.
Indian Standards for Common Cement Grades
| S.No. | IS No. | Products |
| 1. | IS 12330 | Sulphate Resisting Portland Cement |
| 2. | IS 12600 | Low heat Portland Cement |
| 3. | IS 1489 (Part 1) | Portland Pozzolana Cement-Part1 Fly-ash based |
| 4. | IS 1489 (Part 2) | Portland Pozzolana Cement-Part 2 Calcined clay based |
| 5. | IS 269 | Ordinary Portland Cement |
| 6. | IS 3466 | Masonry Cement |
| 7. | IS 455 | Portland Slag Cement |
| 8. | IS 6452 | High Alumina Cement for Structural use |
| 9. | IS 6909 | Super sulphated cement |
| 10. | IS 8041 | Rapid hardening Portland cement |
| 11. | IS 8042 | White Portland Cement |
| 12. | IS 8043 | Hydrophobic Portland Cement |
| 13. | IS 8229 | Oil well Cement |
| 14. | IS 16415: 2015 | Composite Cement- Specification. |
| 15. | IS 16993: 2018 | Microfine Ordinary Portland Cement- Specification. |
| 16. | IS 15895: 2018 | High Alumina Refractory Cement. |
Revision Updates and Latest BIS Amendments
BIS periodically revises standards to match modern construction needs. Plants must stay updated with new test requirements and amendments.
Importance and Benefits of BIS Standards For Cement
BIS Standards for cement ensure that the material used in construction meets consistent quality, strength, and safety benchmarks, helping prevent structural failures and ensuring long-term durability.
Enhanced Durability and Construction Reliability
Structures built using BIS-certified cement display better longevity, reduced cracking, and higher resistance to chemical attacks.
Consumer Trust Through Standardized Quality
Developers, EPC contractors, and government agencies prefer manufacturers who consistently meet BIS norms.
Competitive Advantage for Certified Manufacturers
BIS certification boosts credibility and grants direct access to high-value procurement segments.
Grade-Wise Classification of Cement
Cement is classified grade-wise based on its compressive strength, helping builders choose the right type for specific construction requirements such as residential, commercial, or infrastructure projects.
Overview of OPC Grades (33, 43, 53)
- 33 Grade: Suitable for low-rise buildings
- 43 Grade: Balanced strength and cost
- 53 Grade: High strength for fast-track projects
Classification of PPC, PSC and Composite Cement
Blended cements incorporate fly ash or slag to improve workability and reduce heat of hydration.
How Grade Selection Impacts Construction Use
Different grades serve different applications—plastering, RCC works, mass concreting, infrastructure, and marine structures.
BIS Certification Requirements
BIS Certification requirements ensure that products comply with the quality, safety, and performance standards defined under Indian regulations. Manufacturers must meet specific documentation, testing, and factory audit criteria to obtain approval.
Eligibility Criteria for Cement Manufacturers
A functioning plant, controlled process flow, stable raw materials, and required testing facilities are mandatory.
Mandatory Testing and Quality Control Obligations
Manufacturers must perform regular tests for fineness, strength, setting time, and soundness for every batch.
In-House Laboratory and Calibration Requirements
BIS requires a fully operational lab with calibrated equipment such as Vicat apparatus, Blaine air permeability meter, autoclave, CTM, and chemical testing facilities.
Process and Documents of BIS Certification for Cement
Manufacturers must follow a structured approval system before receiving their BIS License. The process is detailed, but with proper planning, many of our clients have completed certification within 45–60 days.
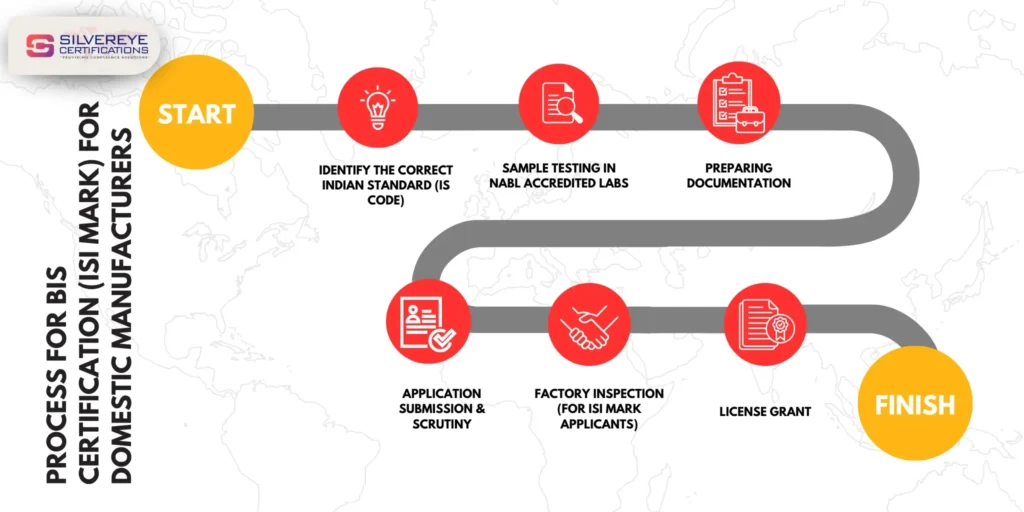
Step-by-Step BIS Certification Procedure
The BIS certification process for cement typically includes:
- Application Filing on the Manak Online Portal
Submission of factory details, product categories, and IS standard selection. - Document Verification
BIS reviews factory layout, machinery details, and QC process. - Sample Testing
BIS officials visit the factory, draw samples, and send them to BIS-recognized labs. - Factory Audit/Inspection
Inspectors verify equipment, testing capabilities, calibration, and production controls. - Test Report Evaluation
Lab results are compared with IS standard requirements. - Grant of License (GoL)
BIS issues the license with a unique CM/L number. - Market Surveillance
BIS conducts ongoing audits and sampling even after certification.
Mandatory Testing and Sample Submission
Cement samples undergo extensive testing, including:
- Fineness
- Standard consistency
- Initial and final setting time
- Compressive strength (3/7/28 days)
- Soundness
- Chemical composition, including lime saturation factor and magnesia content
These tests confirm performance and consistency across multiple time frames. Laboratories accredited by BIS under the Laboratory Recognition Scheme (LRS) are authorized to conduct these tests.
Required Documents for BIS Application
Typical documentation includes:
- Factory registration documents
- Manufacturing process flow chart
- Quality control plan
- Equipment calibration certificates
- Raw material test reports
- In-house lab details
- Employee competence records
- Pollution control certificates
- Packaging artwork with ISI Mark design
A complete and accurate file significantly reduces delays during scrutiny.
BIS License Validity and Renewal
Once granted, a BIS License for Cement remains valid for a defined period, subject to renewal and compliance checks.
Standard Validity Period of BIS License
The initial license is usually valid for two years. Subsequent renewals can extend validity up to five years, depending on compliance performance and timely submission of documentation.
Renewal Procedure and Documentation
The renewal process involves:
- Submission of updated factory details
- Past audit reports
- Production records
- Test reports from in-house and external labs
- Fee payment
Manufacturers must apply for renewal before license expiry to avoid penalties.
Late Fee and Compliance Requirements
Delayed renewal results in:
- Late fees
- Possible suspension of the license
- Mandatory re-inspection in certain cases
Many manufacturers proactively renew six months before expiry to avoid disruptions during peak supply seasons.
BIS Certification Cost and Timeline
The cost of BIS Certification for Cement depends on factory size, number of grades, and testing requirements. Costs generally fall into three categories: BIS fees, testing charges, and audit/travel expenses.
BIS Application Fees and Testing Charges
| Fee Type / Cost Component | Indicative Amount (₹) | Remarks / Source |
| Application fee (new ISI licence) | ₹ 1,000 | Standard non-refundable fee for product certification. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Annual licence fee (domestic manufacturer) | ₹ 1,000 (per year) | Applicable for maintaining ISI licence. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Audit / Factory Inspection fee | ₹ 7,000 per man-day | BIS charges applicable man-day audit fee (for inspection/surveillance) under Scheme I. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Sample testing fee (initial / certification testing) | As applicable | Charges vary depending on number of tests, cement grade (OPC, PPC, PSC), and lab rates. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Marking (Standard-Mark / ISI) fee | As per BIS marking fee schedule | Marking fee depends on IS standard and quantity/volume (cement production volume). (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
| Renewal application fee | ₹ 1,000 (non-refundable) | For licence renewal under standard BIS fee structure. (Bureau of Indian Standards) |
Testing fees vary according to grade selection and lab location.
Factory Inspection and Audit Cost
BIS charges manufacturers for:
- Auditor travel and lodging
- Inspection time
- Additional sampling if required
Remote factories may incur higher inspection costs.
Expected Processing Time for BIS License
Typical timelines:
- Document preparation: 7–10 days
- BIS scrutiny: 10–15 days
- Factory inspection: 15–20 days
- Testing and report review: 10–25 days
Most manufacturers receive the license within 45–60 days with proper planning.
Packaging, Marking & Labeling Rules
The Packaging, Marking & Labeling rules ensure that cement products are packed securely and carry accurate information such as grade, batch number, manufacturing date, and BIS Standard Mark to maintain quality and traceability.
Mandatory ISI Mark and CM/L Number Requirements
Every cement bag must display the ISI mark and license number clearly.
Printing Rules for Cement Bags Under BIS
The IS code, grade, batch number, manufacturer details, and net weight must be printed accurately.
Traceability and Batch Identification Norms
Manufacturers must maintain traceability for every batch through QC and dispatch records.
Conclusion
BIS Standards for Cement form the backbone of India’s construction quality framework. These Indian Standards define strength, safety, chemical limits, and performance expectations for every cement bag manufactured in the country. Manufacturers who follow these standards consistently achieve better market acceptance, fewer quality disputes, and long-term credibility.If you require structured support with BIS Certification, documentation preparation, or audit readiness, the team at Silvereye Certifications can assist you through each stage with industry-aligned guidance and compliance-focused expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are BIS Standards for Cement?
They are official Indian Standards that define the required quality, strength, and chemical limits for different types of cement sold in India.
Why are these standards important?
They ensure consistent cement quality, structural safety, and compliance with national regulations.
Are BIS Standards mandatory?
Yes. Cement cannot be manufactured or sold in India without meeting the applicable BIS Standard and holding a valid ISI licence.
Which major IS codes apply to cement?
Common standards include IS 269, IS 8112, IS 12269, IS 1489 (Part 1 & 2), IS 455, and IS 16415.
What properties do BIS Standards cover?
They cover fineness, setting time, compressive strength, soundness, and chemical limits like magnesia and sulphur trioxide.
Do imported cement products need to follow BIS Standards?
Yes. Imported cement must also comply with the relevant Indian Standards and obtain BIS certification.
What happens if a plant does not meet BIS Standards?
Non-compliance can lead to test failures, licence suspension, penalties, or product seizure.















